Analyses of sewage in Oslo reveal misuse of Ritalin, a medication normally given to patients with ADHD.
Research News - Page 2
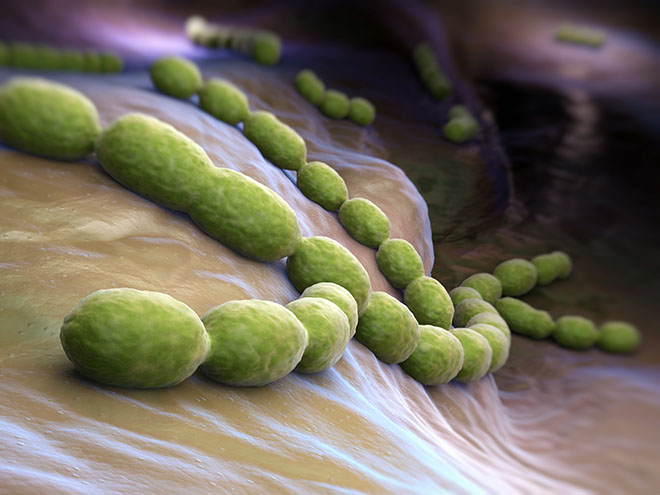
New research is revealing bacteria's internal struggle for power. The result may be better vaccines.
In the future, it will be possible to personalise your cancer treatment to you and your genes. Jian Gao is one of the contributors to the cancer treatment of the future.
Here is the new dietary advice on which types of fat, and in which quantities, are best for your child.
Imagine if we could talk to bacteria and tell them what they should do, or perhaps even better: what they should not do! This scenario is not so distant from what a research group at the University of Oslo (UiO) is working towards
The relations between e-waste and exposure to toxins in Africa has received little research to date. Ruth Prince is part of AnthroTOX, an new interdisciplinary research group combining natural and social sciences to understand and manage global anthropogenic toxicants.
Man-made pollutants, the peculiar immune system of codfish, embryonic development, personalised cancer therapies, human genetic history and new technologies to handle both disease and pollutants. This will be studied in seven new convergence environments at the University of Oslo.
Personalised cancer therapies and human genetic history. These are the topics of the last two convergence environments that will be funded by UiO:Life Science. With this, the list of the seven convergence environments that will receive support in 2017, is complete.
Man-made pollutants, the peculiar immune system of codfish, embryonic development and new technology to handle both disease and pollutants. This will be studied in five new convergence environments at the University of Oslo.
Children born without the ability to get several permanent teeth, known as severe hypodontia, must expect to be "eternal patients". A new doctoral thesis from the Faculty of Dentistry at the University of Oslo has examined how it is possible to better help these children.
There appears to be no end to the health benefits of the much-lauded antioxidants. Now it seems that they can also play a role in whether implants inserted into the body end up being a success or the cause of complications.
Researchers have found a new method to develop antibiotics that are tailored to kill multi-resistant bacteria.
Researchers at the University of Oslo and Oslo University Hospital have discovered that cancer cells grow by stealing energy from neighbouring cells.
A collaboration between the MAGIC non-profit research and innovation programme and the British Medical Journal will enable updated treatment guidelines to reach healthcare professionals more quickly.
Researchers at the Faculty have shown that harmful immune cells are more easily activated in patients suffering from the autoimmune disease lupus than in healthy people.
Interactions between the gut and the body are central to good health. Researchers at the University of Oslo have now identified one of the key regulators of these interactions.
Using low sun protection factor may increase the risk of melanoma. Cutaneous melanoma is one of the most rapidly increasing cancers in Norway and is becoming a major public health challenge.
The Neanderthals lacked several of the genes that can lead to schizophrenia. Does this mean that the genes for schizophrenia are linked to what makes the human species so successful?
Three out of four people could avoid knee surgery with a new form of exercise therapy, with significant cost savings for society.
It is well known that the drug ASA, also known internationally as Aspirin, has analgesic and fever-reducing properties. However, this drug may also increase the likelihood of surviving colon cancer.
The immune defence systems of healthy individuals may become key to future cancer treatment.
Can knowledge about one disease help us to find treatment for another disease?
Together with an international research group, Bente Halvorsen, Professor of Medicine at the University of Oslo, has found a new and effective way to treat hardening of the arteries. The idea came from an unexpected source.
“Oh, you're so hormonal!". We all understand what that means: moody and volatile. But hormones do much more than influence our mood. Without hormones our bodies simply would not function.
British Reuters visited the research group of Professor P?l Rongved at the School of Pharmacy and has made a video about the group's cutting edge technology against antibiotic-resistant bacteria.